
Context
This cluster uses containerd as CRI runtime.
Containerd's default runtime handler is runc. Containerd has been prepared to support an additional runtime handler, runsc (gVisor).
Task
Create a RuntimeClass named sandboxed using the prepared runtime handler named runsc.
Update all Pods in the namespace server to run on gVisor.

Create a RuntimeClass named gvisor-rc using the prepared runtime handler named runsc.
Create a Pods of image Nginx in the Namespace server to run on the gVisor runtime class
You can switch the cluster/configuration context using the following command:
[desk@cli] $ kubectl config use-context prod-account
Context:
A Role bound to a Pod's ServiceAccount grants overly permissive permissions. Complete the following tasks to reduce the set of permissions.
Task:
Given an existing Pod named web-pod running in the namespace database.
1. Edit the existing Role bound to the Pod's ServiceAccount test-sa to only allow performing get operations, only on resources of type Pods.
2. Create a new Role named test-role-2 in the namespace database, which only allows performing update operations, only on resources of type statuefulsets.
3. Create a new RoleBinding named test-role-2-bind binding the newly created Role to the Pod's ServiceAccount.
Note: Don't delete the existing RoleBinding.
Create a Pod name Nginx-pod inside the namespace testing, Create a service for the Nginx-pod named nginx-svc, using the ingress of your choice, run the ingress on tls, secure port.
Create a PSP that will prevent the creation of privileged pods in the namespace.
Create a new PodSecurityPolicy named prevent-privileged-policy which prevents the creation of privileged pods.
Create a new ServiceAccount named psp-sa in the namespace default.
Create a new ClusterRole named prevent-role, which uses the newly created Pod Security Policy prevent-privileged-policy.
Create a new ClusterRoleBinding named prevent-role-binding, which binds the created ClusterRole prevent-role to the created SA psp-sa.
Also, Check the Configuration is working or not by trying to Create a Privileged pod, it should get failed.
a. Retrieve the content of the existing secret named default-token-xxxxx in the testing namespace.
Store the value of the token in the token.txt
b. Create a new secret named test-db-secret in the DB namespace with the following content:
username: mysql
password: password@123
Create the Pod name test-db-pod of image nginx in the namespace db that can access test-db-secret via a volume at path /etc/mysql-credentials
Fix all issues via configuration and restart the affected components to ensure the new setting takes effect.
Fix all of the following violations that were found against the API server:-
a. Ensure that the RotateKubeletServerCertificate argument is set to true.
b. Ensure that the admission control plugin PodSecurityPolicy is set.
c. Ensure that the --kubelet-certificate-authority argument is set as appropriate.
Fix all of the following violations that were found against the Kubelet:-
a. Ensure the --anonymous-auth argument is set to false.
b. Ensure that the --authorization-mode argument is set to Webhook.
Fix all of the following violations that were found against the ETCD:-
a. Ensure that the --auto-tls argument is not set to true
b. Ensure that the --peer-auto-tls argument is not set to true
Hint: Take the use of Tool Kube-Bench
Documentation
Installing the Sidecar, PeerAuthentication, Deployments
You must connect to the correct host . Failure to do so may result in a zero score.
[candidate@base] $ ssh cks000041
Context
A microservices-based application using unencrypted Layer 4 (L4) transport must be secured with Istio.
Task
Perform the following tasks to secure an existing application's Layer 4 (L4) transport communication using Istio.
Istio is installed to secure Layer 4 (L4) communications.
You may use your browser to access Istio's documentation.
First, ensure that all Pods in the mtls namespace have the istio-proxy sidecar injected.
Next, configure mutual authentication in strict mode for all workloads in the mtls namespace.
Secrets stored in the etcd is not secure at rest, you can use the etcdctl command utility to find the secret value
for e.g:-
ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl get /registry/secrets/default/cks-secret --cacert="ca.crt" --cert="server.crt" --key="server.key"
Output
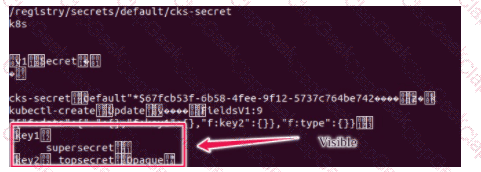
Using the Encryption Configuration, Create the manifest, which secures the resource secrets using the provider AES-CBC and identity, to encrypt the secret-data at rest and ensure all secrets are encrypted with the new configuration.
Context:
Cluster: gvisor
Master node: master1
Worker node: worker1
You can switch the cluster/configuration context using the following command:
[desk@cli] $ kubectl config use-context gvisor
Context: This cluster has been prepared to support runtime handler, runsc as well as traditional one.
Task:
Create a RuntimeClass named not-trusted using the prepared runtime handler names runsc.
Update all Pods in the namespace server to run on newruntime.
Documentation Deployment, Pod, Namespace
You must connect to the correct host . Failure to do so may result in a zero score.
[candidate@base] $ ssh cks000028
Context
You must update an existing Pod to ensure the immutability of its containers.
Task
Modify the existing Deployment named lamp-deployment, running in namespace lamp, so that its containers:
. run with user ID 20000
. use a read-only root filesystem
. forbid privilege escalation
The Deployment's manifest file con be found at /home/candidate/finer-sunbeam/lamp-deployment.yaml.
Context
A PodSecurityPolicy shall prevent the creation of privileged Pods in a specific namespace.
Task
Create a new PodSecurityPolicy named prevent-psp-policy,which prevents the creation of privileged Pods.
Create a new ClusterRole named restrict-access-role, which uses the newly created PodSecurityPolicy prevent-psp-policy.
Create a new ServiceAccount named psp-restrict-sa in the existing namespace staging.
Finally, create a new ClusterRoleBinding named restrict-access-bind, which binds the newly created ClusterRole restrict-access-role to the newly created ServiceAccount psp-restrict-sa.
Context:
Cluster: prod
Master node: master1
Worker node: worker1
You can switch the cluster/configuration context using the following command:
[desk@cli] $ kubectl config use-context prod
Task:
Analyse and edit the given Dockerfile (based on the ubuntu:18:04 image)
/home/cert_masters/Dockerfile fixing two instructions present in the file being prominent security/best-practice issues.
Analyse and edit the given manifest file
/home/cert_masters/mydeployment.yaml fixing two fields present in the file being prominent security/best-practice issues.
Note: Don't add or remove configuration settings; only modify the existing configuration settings, so that two configuration settings each are no longer security/best-practice concerns.
Should you need an unprivileged user for any of the tasks, use user nobody with user id 65535
Enable audit logs in the cluster, To Do so, enable the log backend, and ensure that
1. logs are stored at /var/log/kubernetes-logs.txt.
2. Log files are retained for 12 days.
3. at maximum, a number of 8 old audit logs files are retained.
4. set the maximum size before getting rotated to 200MB
Edit and extend the basic policy to log:
1. namespaces changes at RequestResponse
2. Log the request body of secrets changes in the namespace kube-system.
3. Log all other resources in core and extensions at the Request level.
4. Log "pods/portforward", "services/proxy" at Metadata level.
5. Omit the Stage RequestReceived
All other requests at the Metadata level
Documentation
Deployment, Pod Security Admission, Pod Security Standards
You must connect to the correct host . Failure to do so may result in a zero score.
[candidate@base] $ ssh cks000036
Context
For compliance, all user namespaces enforce the restricted Pod Security Standard .
Task
The confidential namespace contains a Deployment that is not compliant with the restricted Pod Security Standard . Thus, its Pods can not be scheduled.
Modify the Deployment to be compliant and verify that the Pods are running.
The Deployment's manifest file can be found at /home/candidate/nginx-unprivileged.yaml.
Context
A default-deny NetworkPolicy avoids to accidentally expose a Pod in a namespace that doesn't have any other NetworkPolicy defined.
Task
Create a new default-deny NetworkPolicy named defaultdeny in the namespace testing for all traffic of type Egress.
The new NetworkPolicy must deny all Egress traffic in the namespace testing.
Apply the newly created default-deny NetworkPolicy to all Pods running in namespace testing.



